Excretion and osmoregulation Grade 11 (Class 11) notes pdf (Life Science Grade 11 or Biology Grade 11). On this page, we will be learning about:
Excretion: a process in which metabolic waste is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after leaving the cell. Excretion is an essential process in all forms of life.
and…
Osmoregulation: Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism’s body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism’s water content
Excretion
Understanding Terminologies & definitions on Excretion Topic
Understanding the key terminologies in the topic of Excretion is essential for any learner. Mastering these terms will greatly assist you in exams, tests, and assignments. Below is a list of crucial terms, along with their definitions, linked to reputable sources for further reading.
Important Terminologies in Excretion
- Active Absorption: The process of absorbing substances against the concentration gradient using energy. This is essential in processes like nutrient uptake in cells.
- Ascending Limb: A part of the loop of Henlé in the nephron’s renal tubule that carries waste from the hairpin bend towards the distal convoluted tubule. It’s crucial in the kidney’s ability to concentrate urine.
- Bowman’s Capsule: A cup-shaped structure surrounding the glomerulus in the nephron of the human kidney, involved in the initial stages of filtering blood.
- Calyx: A wide, funnel-like structure in the kidney into which the collecting tubules open, leading to the renal pelvis, which funnels urine into the ureter.
- Descending Limb: Part of the loop of Henlé in the nephron’s renal tubule that carries waste from the proximal convoluted tubule towards the hairpin bend. It plays a role in the concentration of urine.
- Dialysis: A medical procedure for artificially removing waste products from the bloodstream when the kidneys are unable to do so naturally.
- Distal Convoluted Tubule: The twisted portion of the renal tubule furthest from the Malpighian body, involved in the regulation of potassium, sodium, calcium, and pH.
- Duct of Bellini: Tubes formed by the union of the collecting ducts in the kidney, which play a role in concentrating urine before it exits the nephron.
- Excretion: The removal of waste products of metabolism from cells, which is vital for maintaining homeostasis in the body.
- Filtration: The process by which water and small solutes, including metabolic wastes, are extracted from the body fluid and passed into the excretory system. This occurs primarily in the glomerulus of the nephron.
- Glomerulus: A capillary network within Bowman’s capsule of the nephron in the human kidney, also referred to as the first capillary network. It’s essential in the filtration process.
- Loop of Henlé: A region of the nephron of the human kidney which lies between the proximal and distal convoluted tubules. It’s critical for the concentration of urine.
- Malpighian Body: Part of the nephron of the human kidney, made up of Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus, responsible for filtering blood.
- Nephron: The functional unit responsible for excretion and osmoregulation in the kidney, essential for filtering blood and producing urine.
- Passive Absorption: The absorption of substances down a concentration gradient, i.e., from high concentration to low concentration, without the use of energy.
- Podocytes: Specialised cells in the inner layer of Bowman’s capsule in the nephron that assist in the filtration process.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule: The twisted portion of the renal tubule that is closest to the Malpighian body, responsible for the reabsorption of water, ions, and all organic nutrients.
- Renal Artery: A blood vessel carrying oxygenated blood with nitrogenous wastes to the kidney, playing a key role in kidney function.
- Renal Capsule: The thin, fibrous, protective outer covering of the kidney.
- Renal Vein: A blood vessel carrying deoxygenated blood with very little nitrogenous waste away from the kidney.
- Selective Absorption: The absorption of only certain solutes from blood filtrate, occurring in the excretory organs of animals.
- Slit Pores: Tiny pores between the podocytes that form the lining of Bowman’s capsule, enabling the podocytes to act as selective filters.
- Tubular Secretion: The movement of waste substances from the second capillary network into the renal tubule of the nephron in the human body.
- Ureter: The duct that conveys urine from the kidney to the bladder.
- Urethra: A tube that transports urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body.
Understanding the Urinary System
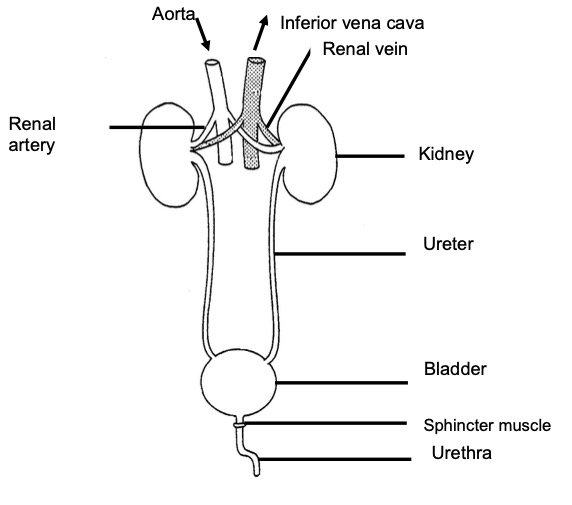
Longitudinal section of a human kidney
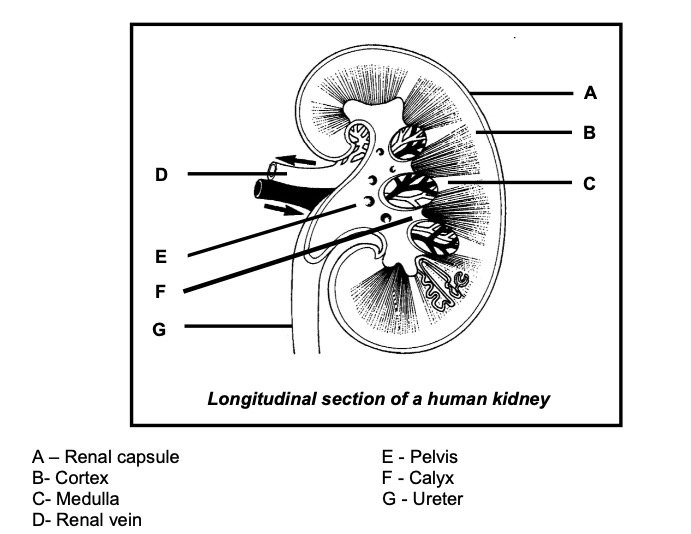
OR
Detailed longitudinal section of a human kidney
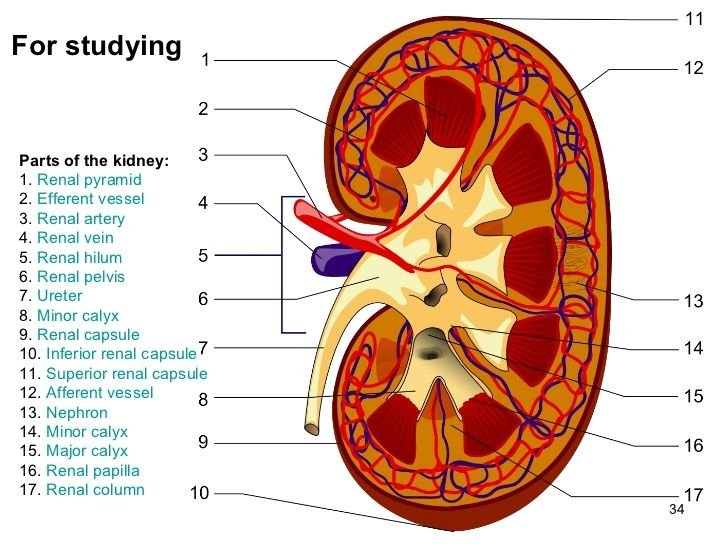
Osmoregulation
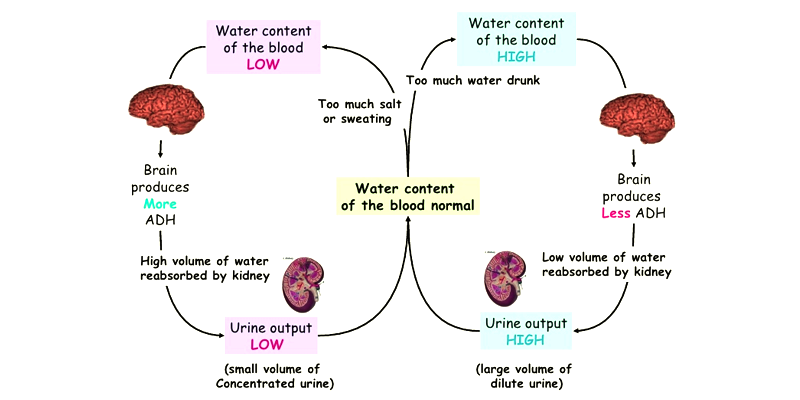
What is Osmoregulation? Osmoregulation is the process of maintaining salt and water balance (osmotic balance) across membranes within the body. The fluids inside and surrounding cells are composed of water, electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. An electrolyte is a compound that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water. A nonelectrolyte, in contrast, does not dissociate into ions in water. The body’s fluids include blood plasma, fluid that exists within cells, and the interstitial fluid that exists in the spaces between cells and tissues of the body. The membranes of the body (both the membranes around cells and the “membranes” made of cells lining body cavities) are semipermeable membranes. Semipermeable membranes are permeable to certain types of solutes and to water, but typically cell membranes are impermeable to solutes. Source: Open Textbook
Video Lesson on Osmoregulation
Downloadable Notes on Excretion and Osmoregulation for Grade 11
Term 3 Excretion Tasks for Grade 11 Learners
Looking for something specific?
[ivory-search id="163692" title="Default Search Form"]




Leave a Comment