10 Differences Between San and Khoikhoi: The San and Khoikhoi are two distinct groups indigenous to southern Africa, often collectively referred to as the...
The Impact of Migrant Labour System in Black Communities Essay Guide:
Essay
The migrant labour system has been a significant factor in shaping the socioeconomic landscape of black communities. This system, which involves the movement of people from their homes to work in distant places, often for extended periods, has profound impacts on families, local economies, and social structures. In this essay, we explore the various dimensions of how the migrant labour system affects black communities, highlighting both historical and contemporary perspectives.
The Historical Context of the Migrant Labour System
- Origins and Development: The migrant labour system was institutionalised as part of colonial and apartheid-era policies in many countries, aimed at exploiting cheap black labour while enforcing racial segregation.
- Economic Implications: For many black communities, this system was a double-edged sword. It provided essential income for families but also entrenched poverty by depriving communities of their strongest and most productive members.
- Social and Family Dynamics: The prolonged absence of family members led to the breakdown of traditional family structures and community cohesion, affecting the upbringing of children and weakening social bonds.
Economic Impacts on Black Communities
- Remittances and Local Development: One of the positive aspects of the migrant labour system is the flow of remittances back to the workers’ home communities. These funds are crucial for the local economy, often being the primary source of income for many families.
- Dependency and Underdevelopment: However, reliance on remittances has also discouraged local entrepreneurial initiatives and the development of sustainable local economies, perpetuating a cycle of dependency and underdevelopment.
Social and Psychological Effects
- Disruption of Social Fabric: The absence of significant portions of the population, particularly men, has profound effects on the social structure of black communities, leading to issues like the feminisation of rural poverty and increased burdens on women and the elderly.
- Psychological Impact: The system has also taken a psychological toll on the migrant workers and their families, leading to feelings of alienation, stress, and the strain of living in two worlds.
The Role of Policy and Advocacy
- Need for Policy Intervention: Addressing the adverse effects of the migrant labour system on black communities requires comprehensive policy interventions aimed at improving living and working conditions for migrant workers and fostering economic development in their home communities.
- Advocacy and Empowerment: Civil society organizations and community advocates play a critical role in raising awareness about the issues faced by migrant workers and lobbying for changes in policies and practices to support the well-being of black communities.
Conclusion
The impact of the migrant labour system on black communities is multifaceted, with deep historical roots and complex socio-economic consequences. While it has provided necessary economic support for many families, it has also contributed to social disintegration and economic disparities. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from governments, civil society, and the communities themselves to create a more equitable and sustainable future for all affected by the migrant labour system.
Facts to Consider about The Impact of the Migrant Labour System

Integrating specific years and periods can provide a clearer historical timeline for the impact of the migrant labour system on black communities. Let’s incorporate these details into the previously mentioned facts:
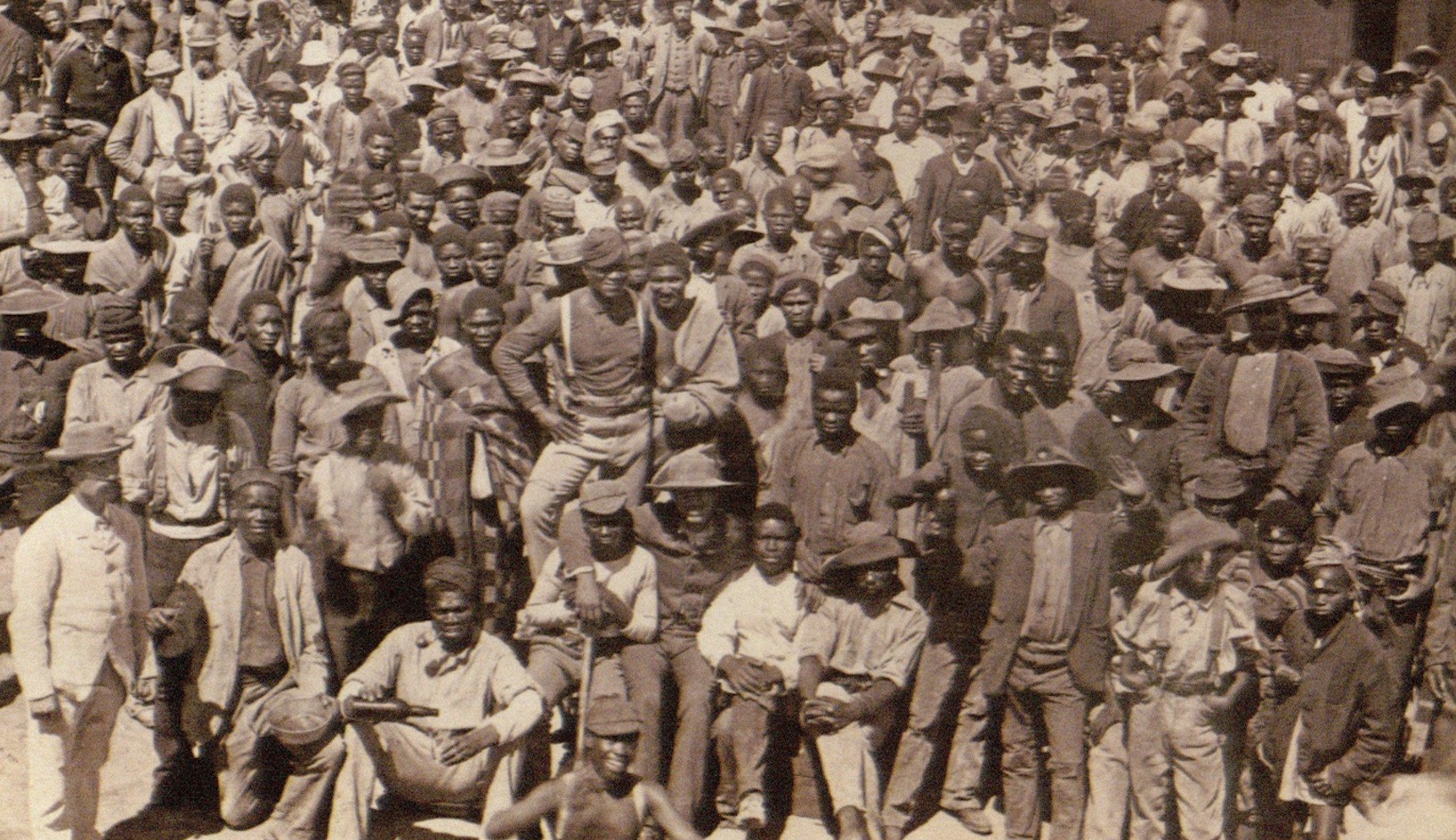
- Colonial Beginnings (17th-19th Centuries): The foundations of the migrant labour system were laid during colonial expansion into Africa, where European powers sought cheap labor for agricultural and mining operations.
- Apartheid Era (1948-1994): South Africa’s apartheid regime formalized the migrant labour system, mandating racial segregation and controlling black South Africans’ movement through pass laws.
- Gold and Diamond Rushes (Late 19th Century): The discovery of gold (1886) and diamonds (1867) in South Africa significantly increased the demand for migrant labor, drawing workers from across the continent.
- Men as Primary Migrants (Throughout the 20th Century): The pattern of men engaging in migrant labor, particularly in mining and industrial sectors, persisted throughout the 20th century, impacting family structures across generations.
- Single-Sex Hostels (20th Century): Established primarily during the 20th century, these hostels housed migrant workers in cities and mining towns, segregating them from their families for extended periods.
- The Homelands System (1951-1994): South Africa’s Bantu Authorities Act of 1951 established “homelands” or Bantustans, forcing black South Africans into designated rural areas intended to serve as labor reservoirs for urban industrial centers.
- Migrant Labour in Southern Rhodesia/Zimbabwe (Early 20th Century): The British South Africa Company introduced a tax in cash in 1894, forcing black men into the colonial economy as migrant laborers, a system that expanded significantly throughout the 20th century.
- Migrant Workers in Zambia’s Copperbelt (1930s-1970s): The development of copper mining in Zambia attracted large numbers of migrant workers, particularly during the copper boom years following World War II.
- Pass Laws in South Africa (1952): The Abolition of Passes and Coordination of Documents Act (1952) required all black South Africans over the age of 16 to carry a “pass” at all times, a key element of the migrant labor system under apartheid.
- Creation of the African Mineworkers’ Union (1941): The formation of the African Mineworkers’ Union in South Africa was a significant response to the exploitation under the migrant labour system, culminating in the miners’ strike of 1946.
- Lesotho and the Migrant Labour System (20th Century): Lesotho became a significant source of migrant labor for South African mines, with remittances from miners working in South Africa playing a crucial role in Lesotho’s economy.
- Independence Movements (Mid-20th Century): The period of decolonization across Africa (1950s-1970s) saw newly independent states grappling with the legacy of migrant labor systems imposed during colonial rule.
- Sharpeville Massacre (1960): The Sharpeville Massacre in South Africa, where police opened fire on a crowd protesting the pass laws, highlighted the brutal enforcement of the migrant labour system.
- Urbanization Trends (Post-1945): The end of World War II marked a significant increase in urbanization in Africa, driven partly by the migrant labor system, as people moved to cities in search of work.
- Transition to Democracy in South Africa (1994): The end of apartheid and South Africa’s transition to democracy in 1994 marked a significant shift, although the legacy of the migrant labour system continues to affect black communities.
These historical facts, with specific years and periods, offer a more detailed timeline of how the migrant labour system has impacted black communities over the centuries.
Essay Guide and Tips
To enhance the quality and impact of your essay on “The Impact of Migrant Labour System in Black Communities”, consider incorporating the following seven tips into your writing process:
- Incorporate Personal Narratives:
- Example: Include stories or interviews from individuals who have experienced the migrant labour system firsthand. This approach adds a personal dimension to your essay, making the impacts more relatable and compelling to the reader.
- Use Data and Statistics:
- Example: Incorporate relevant statistics on employment trends, remittance flows, and socioeconomic changes within black communities to provide evidence-based support for your arguments.
- Compare and Contrast:
- Example: Analyse the differences in the impact of the migrant labour system across various regions or countries. This can highlight how local policies and the historical context influence the system’s effects on black communities.
- Discuss Policy Solutions:
- Example: Include a section on potential policy interventions and best practices from other contexts that could mitigate the negative impacts of the migrant labour system. Suggest how these could be adapted for black communities.
- Incorporate Theoretical Frameworks:
- Example: Apply sociological or economic theories to your analysis to deepen the understanding of why the migrant labour system exists and its effects on black communities. This could involve theories of migration, economic dependency, or social capital.
- Highlight Community Initiatives:
- Example: Showcase examples of how black communities themselves are responding to the challenges posed by the migrant labour system, such as through local economic development projects or social support networks.
- Engage with Counterarguments:
- Example: Acknowledge and critically evaluate the arguments supporting the benefits of the migrant labour system, such as economic necessity or development opportunities. This balanced approach demonstrates critical thinking and deepens the essay’s analysis.
By integrating these tips into your essay, you’ll enrich your analysis, making it more dynamic, evidence-based, and engaging for your audience. This approach not only demonstrates a thorough understanding of the topic but also showcases your ability to think critically and empathetically about the complex impacts of the migrant labour system on black communities.