Rate of Reaction Grade 12 Notes pdf
Rate of reaction grade 12 notes pdf:
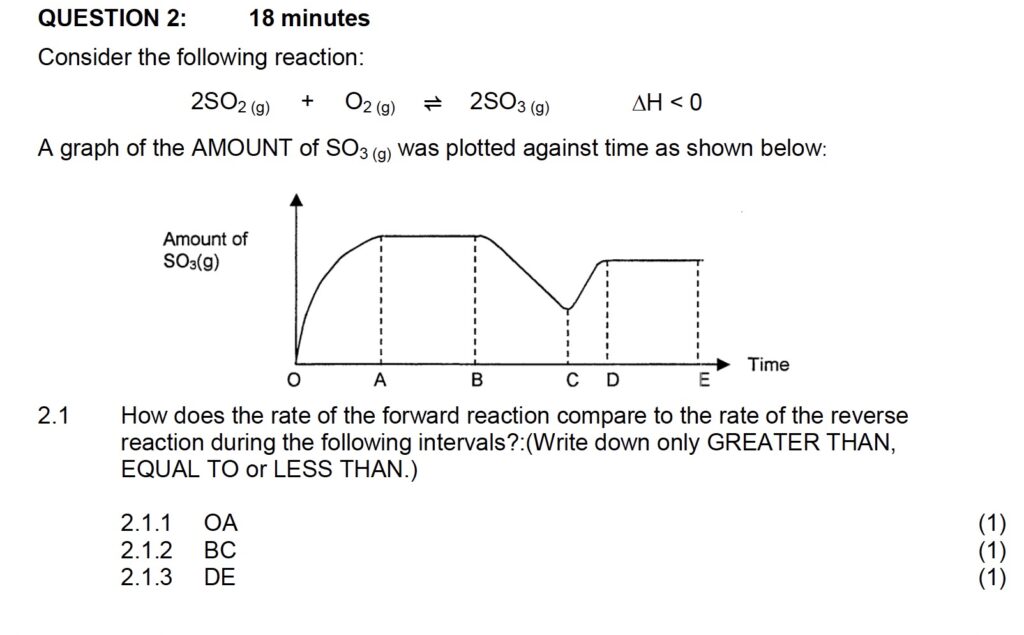
“Rate of Reaction” for Grade 12, especially in the context of Physical Sciences Paper 2, typically explores how quickly reactants are converted into products in a chemical reaction. This topic is a crucial part of the curriculum as it ties in with understanding chemical kinetics, which is the study of the rates of chemical processes.
The key areas covered often include:
- Factors Affecting Reaction Rates: These include the concentration of reactants, temperature, surface area of solid reactants, and the presence of catalysts.
- Rate Laws: These are mathematical equations that describe the relationship between the concentration of reactants and the rate of reaction.
- Reaction Mechanisms: This involves the step-by-step sequence by which reactants actually transform into products.
- Activation Energy: The minimum energy that reactant molecules must possess for a reaction to occur.
For students, having access to downloadable notes can be super helpful. These notes would ideally provide clear explanations, example problems, and diagrams to illustrate concepts like reaction profiles and the effect of catalysts on activation energy. Additionally, practice questions at the end of each section can help reinforce learning and prepare students for their exams.
Downloadable Notes
Rate of reaction Grade 12 questions and answers
Below is a list of questions and answers on the topic of Rate of Reaction for Grade 12 students. These can be useful for studying or testing knowledge in this area of physical sciences.
Question 1:
What is the effect of increasing the concentration of reactants on the rate of a chemical reaction? Explain.
Answer:
Increasing the concentration of reactants generally increases the rate of a chemical reaction. This happens because a higher concentration of reactants leads to more frequent collisions among the reactant molecules, thereby increasing the likelihood of effective collisions that convert reactants into products.
Question 2:
Describe how temperature affects the rate of a chemical reaction and explain why this happens.
Answer:
Temperature usually has a significant effect on the rate of chemical reactions; as the temperature increases, the reaction rate also increases. This occurs because higher temperatures provide more energy to the reactant molecules, which increases their movement and the number of effective collisions. Additionally, higher energy means more molecules can overcome the activation energy barrier needed for the reaction to proceed.
Question 3:
What is meant by ‘activation energy’ in a chemical reaction?
Answer:
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that the reacting particles must possess for a reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that must be overcome for reactants to be transformed into products. Lowering the activation energy, such as by adding a catalyst, can increase the reaction rate.
Question 4:
Explain the role of a catalyst in a chemical reaction.
Answer:
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the reaction. It works by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy compared to the uncatalyzed reaction. This allows more reactant molecules to participate in the reaction at a given temperature, thereby increasing the reaction rate.
Question 5:
The reaction between sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid is a popular experiment to observe reaction rates. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction and describe a method to measure its rate.
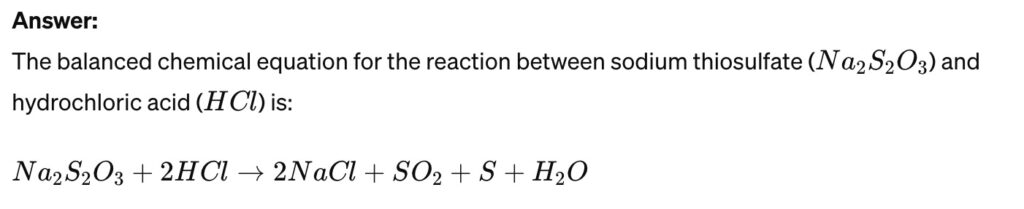
To measure the rate of this reaction, you can observe the formation of a yellow sulfur precipitate, which clouds the solution. Measuring how quickly the solution becomes opaque (e.g., by timing how long it takes for a mark under the container to become invisible when viewed from above) provides a way to gauge the reaction rate. Adjusting factors like concentration or temperature and measuring how these changes affect the time taken for the solution to become opaque can also be used to study the effect of these variables on the reaction rate.

Useful Formulas
For students studying the rate of reaction in Grade 12 Physical Sciences, there are several key formulas that are essential to understand and apply. These formulas help in calculating various aspects of chemical kinetics. Here are some of the most important ones:
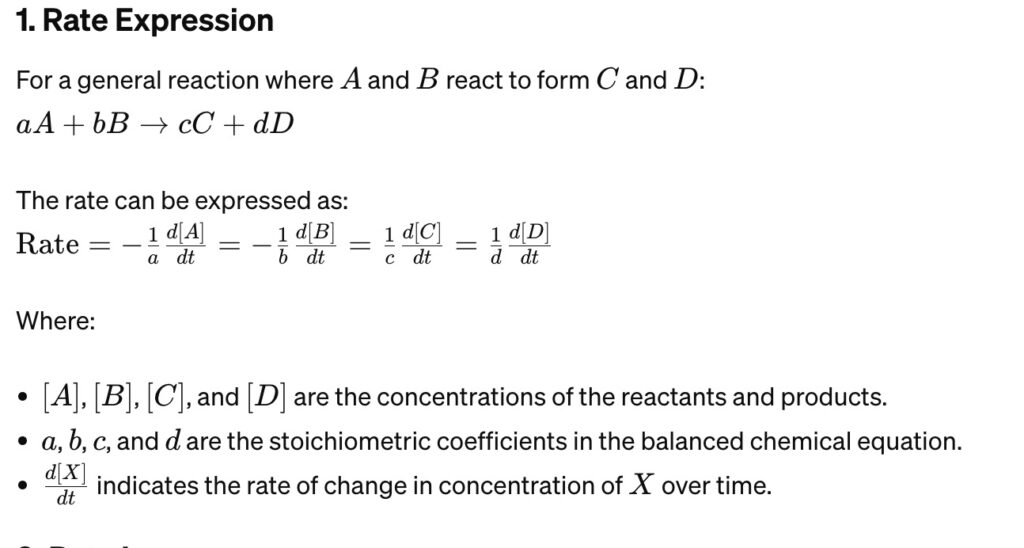
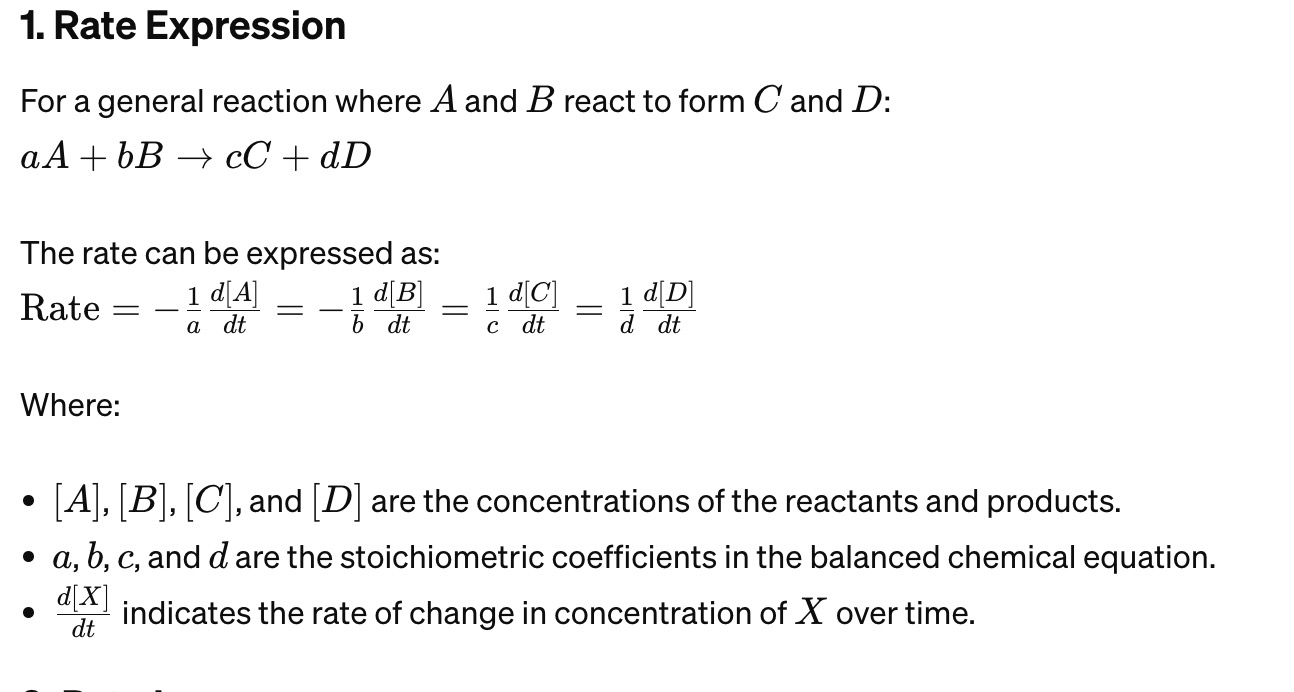
Rate Expression Formula