Tropical Cyclone Freddy – Geography Grade 12 Research Task

On this page, we have compiled a general guide for Grade 12 Geography Students who are doing their research on Tropical Cyclone Freddy.
In this educational article, we will delve into the complex dynamics of Tropical Cyclone Freddy, a powerful weather system that posed significant threats and caused substantial impacts across various regions, notably Madagascar, Mozambique, and Malawi. This task will explore the formation, path, and consequences of Freddy, offering insights into the broader subject of tropical cyclones.
Tropical Cyclone Freddy
Tropical Cyclone Freddy stands as a significant weather event in the 2023 cyclone season, illustrating the potent force and extensive impact tropical cyclones can have on regions. Initially developing in the Indian Ocean, Freddy quickly intensified, showcasing the rapid and formidable growth capability of such storms. It made its mark by impacting multiple countries, with notable effects on Madagascar, Mozambique, and Malawi.
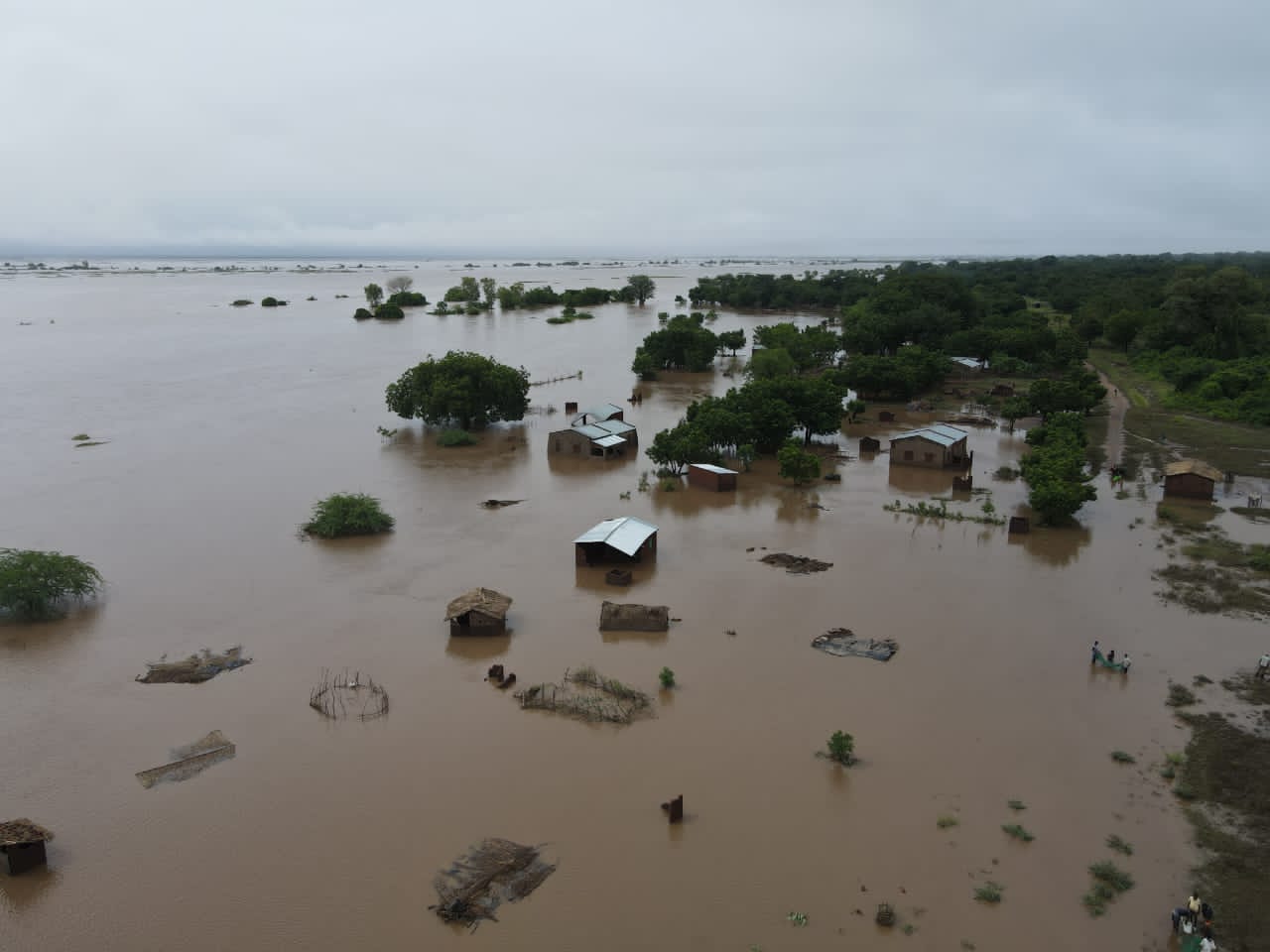
In Madagascar, Freddy made landfall on 21 February, near Mananjary, bringing with it powerful winds of up to 130 km/h and gusts of 180 km/h, causing widespread damage, including a storm surge and significant structural damage to homes and infrastructure. The cyclone’s arrival compounded challenges in regions already vulnerable from previous cyclonic activities and ongoing recovery efforts, exacerbating flood risks in areas with saturated soils from Cyclone Cheneso.
The cyclone’s path then took it across the Mozambique Channel, where it made a second landfall in Mozambique on 11 March, particularly affecting the Zambezia Province. Despite weakening to a tropical depression, Freddy continued to unleash heavy rains and strong winds, leading to extensive flooding, displacement of thousands, and destruction of homes and infrastructure. The cumulative rainfall in some areas reached more than what is typically expected in a month, stressing the critical situation in regions already dealing with the aftermath of previous weather-related disasters.
Freddy‘s impact extended to Malawi, where it has been associated with severe weather conditions, including intense rainfall leading to mudslides and floods, particularly in the southern region. The cyclone’s effects have been devastating, with significant loss of life, displacement of communities, and damage to property and livelihoods. The government’s declaration of a State of Disaster in affected districts underscores the severity of the situation.
The trajectory and effects of Tropical Cyclone Freddy underline the complex challenges posed by such natural disasters in the context of global warming, which is believed to influence the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones. Freddy exemplifies the urgent need for robust disaster preparedness, response mechanisms, and long-term strategies to mitigate the impact of similar future events on vulnerable communities.
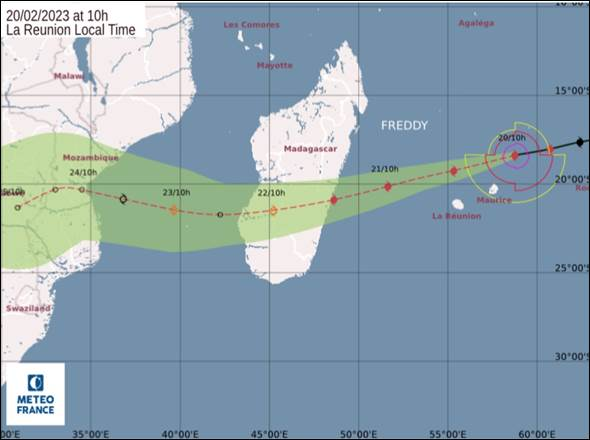
Map indicating the path of the tropical cyclone Freddy
Why do tropical cyclones such as Freddy develop in late summer?
Tropical cyclones like Freddy tend to develop in late summer due to the optimal conditions present during this time—warm sea temperatures and high humidity levels. These conditions are crucial for cyclone formation, providing the energy necessary for these systems to intensify.
What is the impact of coriolis force and latent heat on the development of tropical cyclone Freddy?
The development of Tropical Cyclone Freddy was significantly influenced by the Coriolis force and latent heat. The Coriolis force, resulting from the Earth’s rotation, imparts a spinning motion to the storm, while the release of latent heat during condensation provides the energy that fuels the cyclone’s intensification.
Discussing the stage of development of the tropical cyclone Freddy.
Tropical Cyclone Freddy exhibited rapid intensification as it moved across the Indian Ocean. It reached its peak intensity just before making landfall, characterized by sustained winds and heavy rainfall. Freddy’s development showcased the dynamic and powerful nature of tropical cyclones under conducive environmental conditions.
Why can category 1 tropical cyclones be more destructive (damaging) than category 5 tropical cyclones?
Category 1 tropical cyclones can be more destructive than their Category 5 counterparts under certain circumstances. Factors such as slow movement over populated areas, leading to prolonged wind and rain exposure, and the specific vulnerability of the impacted regions can amplify the damage caused by lower-category cyclones.
How did tropical cyclone Freddy impact the following?
Environment
Tropical Cyclone Freddy caused widespread environmental destruction, including flooding and landslides. These impacts were exacerbated in Madagascar, where soils were already saturated from previous cyclones, leading to significant flood risks.
Economy
The economies of the affected regions suffered greatly due to Tropical Cyclone Freddy. Infrastructure damage, agricultural losses, and the disruption of commerce and tourism were notable economic consequences of the cyclone.
People/Communities
The human toll was significant, with fatalities, displacements, and extensive damage to homes and communities. In Madagascar, Mozambique, and Malawi, thousands were left homeless or displaced, highlighting the devastating impact of Freddy on local populations.
What precautions can be implemented/ or has been implemented to reduce the impact of the tropical cyclone.
The local government/Government of the country
Governments implemented early warning systems, evacuation plans, and post-disaster relief efforts. In anticipation of Freddy, preemptive evacuations and the suspension of schools and public transport were notable measures taken to mitigate the cyclone’s impact.
The local residents
Residents were advised to secure property, stock emergency supplies, and adhere to evacuation orders. Community awareness and preparedness initiatives were crucial in minimizing the cyclone’s human and material toll.
Evaluating the impact of Global Warming on the frequency (regularity) of tropical cyclones such as Freddy.
Global warming is believed to influence the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones. Warmer sea temperatures can lead to more frequent and more potent cyclones, as seen with Tropical Cyclone Freddy. The increasing regularity and severity of such weather events highlight the urgent need for climate action.
The Path of Tropical Cyclone Freddy
Formation and Initial Intensification
Tropical Cyclone Freddy formed in the Indian Ocean in early February 2023. Displaying rapid intensification, it became a major concern for meteorologists and disaster preparedness officials due to its trajectory towards populated landmasses. This phase of Freddy’s path was marked by the accumulation of immense energy, fueled by warm ocean waters and conducive atmospheric conditions.
First Landfall in Madagascar
On 21 February, Freddy made its initial landfall on the eastern coast of Madagascar, near Mananjary. By this time, Freddy had achieved significant strength, with sustained average winds of 130 km/h and gusts of up to 180 km/h. This initial landfall was particularly devastating due to the pre-existing conditions in the region; soils were already saturated from the recent Cyclone Cheneso, exacerbating the flood risk and leading to widespread environmental and infrastructural damage.
Movement Across the Mozambique Channel
After crossing Madagascar, Freddy continued its path across the Mozambique Channel. During this phase, it maintained considerable strength, posing an imminent threat to mainland Africa. The cyclone’s trajectory through the channel was closely monitored as it aimed for a second landfall on the continent.
Second Landfall in Mozambique
Tropical Cyclone Freddy made its second landfall in Mozambique on 11 March, particularly affecting the Zambezia Province. Despite weakening to a tropical depression by the time of landfall, Freddy continued to generate intense rainfall across the region. This resulted in severe flooding, displacement of communities, and extensive damage to property and infrastructure. The impact in Mozambique highlighted the cyclone’s enduring power and the challenges of managing cyclone-related disasters in vulnerable regions.
Impact Beyond Landfall
The influence of Tropical Cyclone Freddy extended beyond its landfall points, affecting regions in southern Malawi with heavy rains and strong winds. The widespread nature of Freddy’s impacts underlines the extensive reach of tropical cyclones, capable of affecting areas far from the initial landfall site through associated weather patterns and rainfall.
Conclusion/Summary
Tropical Cyclone Freddy serves as a stark reminder of the destructive potential of tropical cyclones and the importance of preparedness and mitigation strategies. Its journey through Madagascar, Mozambique, and Malawi underscores the challenges posed by such natural disasters in the era of global warming. Personal reflections on the impact of tropical cyclones reveal a blend of awe for nature’s power and a resolve for better resilience and adaptive measures in the face of future storms.

[…] Tropical cyclones Freddy […]