This comprehensive guide, titled “Geography Grade 10 Questions and Answers PDF Term 3,” aims to address the critical environmental and societal issues covered in...
Life Science Grade 10 June Exam Questions and Answers:
2024 Questions and Answers
SET 1
The axial skeleton is made up of the following regions
- A) Skull, vertebral column, and hip bones
- B) Skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum
- C) Skull, pectoral girdle, ribs, and sternum
- D) Skull, pelvic girdle, ribs, and sternum
The building blocks of proteins are …
- A) disaccharides
- B) monosaccharides
- C) amino acids
- D) glycerol
The mitochondria are the site of …
- A) photosynthesis
- B) cellular respiration
- C) cellular division
- D) cytokinesis
The following is true about enzymes except for one of the following options
- A) Enzymes are denatured at extreme temperatures
- B) Enzymes are denatured at extreme pH
- C) Enzymes are used up in a chemical reaction
- D) Enzymes control and regulate all chemical reactions that take place in a cell
Protein substance produced by the body to fight against disease
- A) Enzyme
- B) Microbes
- C) Bacterium
- D) Antibody
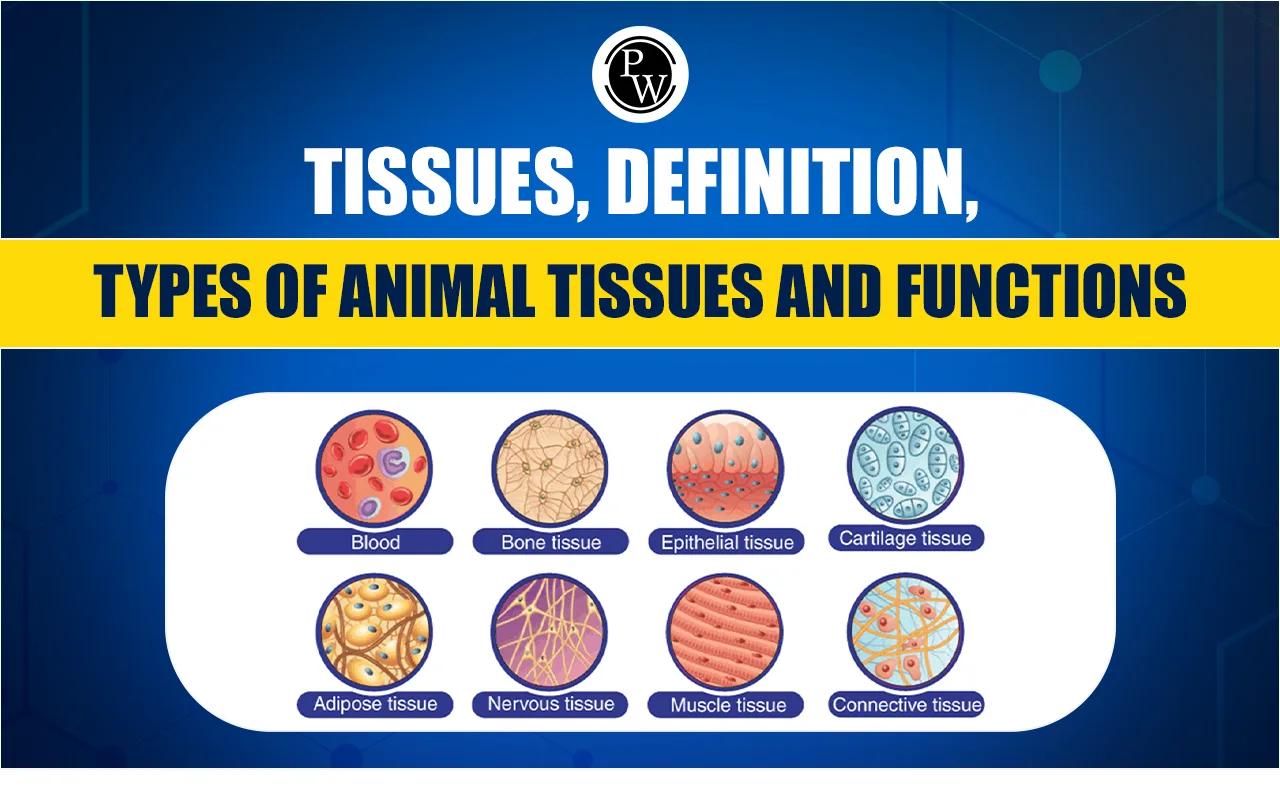
Connective tissue that reduces friction between bones:
- A) Cartilage
- B) Tendon
- C) Ligament
- D) Blood
The tendency of liquids to move up narrow tubes is called …
- A) capillarity action
- B) transpiration
- C) root pressure
- D) transpiration pull
Epithelial tissues lining the mouth and lungs is known as. . . . . tissues
- A) Cuboidal
- B) Columnar
- C) Ciliated columnar
- D) Squamous
The type of root system in dicotyledonous plants
- A) Adventitious roots
- B) Tap roots
- C) Lateral roots
- D) Immature root
The series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into 4 daughter cells
- A) Differentiation
- B) Karyokinesis
- C) Meiosis
- D) Cell cycle
Correct Answer Guide:
- The axial skeleton: B) Skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum
- Building blocks of proteins: C) amino acids
- Site of mitochondria: B) cellular respiration
- True about enzymes except: C) Enzymes are used up in a chemical reaction
- Protein substance against disease: D) Antibody
- Reduces friction between bones: A) Cartilage
- Tendency of liquids to move up tubes: A) capillarity action
- Epithelial tissues: D) Squamous
- Root system in dicotyledonous plants: B) Tap roots
- Events causing cell division into 4 cells: C) Meiosis
SET 2
The primary function of red blood cells is to …
- A) Fight infections
- B) Carry oxygen
- C) Clot blood
- D) Remove waste
Which vitamin is crucial for the absorption of calcium?
- A) Vitamin B12
- B) Vitamin C
- C) Vitamin D
- D) Vitamin E
What is the main energy source for the human body?
- A) Proteins
- B) Carbohydrates
- C) Fats
- D) Vitamins
The hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels is …
- A) Insulin
- B) Adrenaline
- C) Cortisol
- D) Estrogen
Which organ is primarily responsible for detoxification and metabolism?
- A) Heart
- B) Liver
- C) Kidneys
- D) Stomach
Nerve cells are also known as …
- A) Neurons
- B) Nephrons
- C) Leukocytes
- D) Myocytes
The process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy is called …
- A) Glycolysis
- B) Photosynthesis
- C) Fermentation
- D) Respiration
Which type of joint allows for rotation and bending movements?
- A) Hinge joint
- B) Pivot joint
- C) Ball and socket joint
- D) Saddle joint
The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism is a …
- A) Cell
- B) Tissue
- C) Organ
- D) System
A genetic disorder characterized by the absence of pigment in skin, hair, and eyes is called …
- A) Hemophilia
- B) Albinism
- C) Down syndrome
- D) Cystic fibrosis
Correct Answer Guide:
- Primary function of red blood cells: B) Carry oxygen
- Vitamin crucial for calcium absorption: C) Vitamin D
- Main energy source for the human body: B) Carbohydrates
- Hormone regulating blood sugar levels: A) Insulin
- Organ responsible for detoxification: B) Liver
- Nerve cells are known as: A) Neurons
- Plants converting light to chemical energy: B) Photosynthesis
- Type of joint for rotation and bending: C) Ball and socket joint
- Smallest structural and functional unit: A) Cell
- Genetic disorder with absence of pigment: B) Albinism
SET 4
Briefly explain TWO functions of the skeleton
List TWO functions of proteins in a diet
What is meant by saturated fatty acids? And suggest a reason why eating too many saturated fatty acids is unhealthy
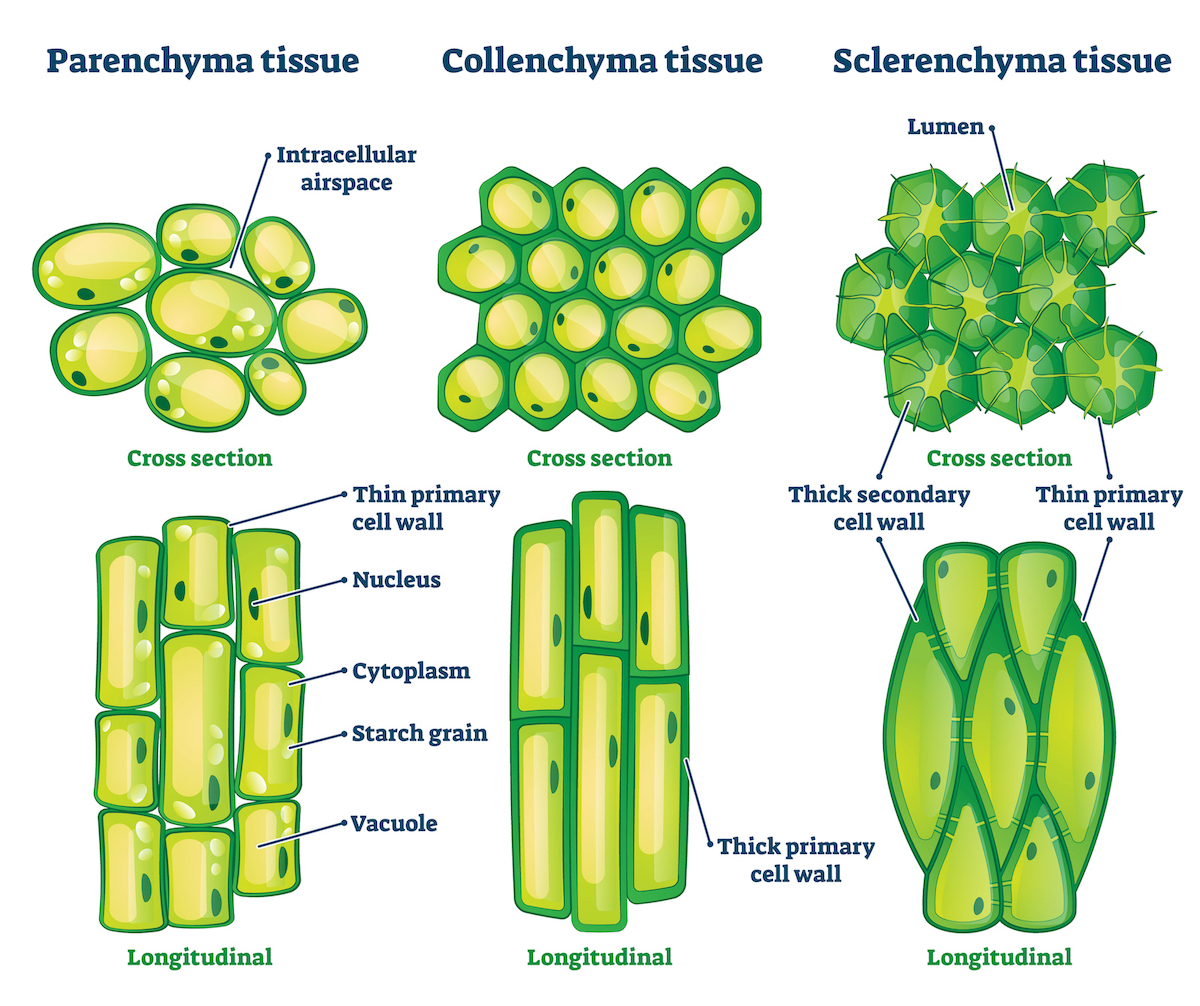
Xylem is a conducting tissue found in leaves. List THREE structural features of xylem that allow it to perform its function
Suggest two biological importance of mitosis
Give ONE difference in telophase between plant and animal cells
Cancer is described as the uncontrollable division of cells.
- (a) State THREE causes of cancer
- (b) State TWO types of treatment used for cancer
Answers:
- Functions of the Skeleton:
- Support: The skeleton provides structural support for the body.
- Protection: The skeleton protects critical internal organs.
- Functions of Proteins in a Diet:
- Tissue Repair and Growth: Proteins are crucial for the repair and growth of body tissues.
- Enzymatic and Hormonal Functions: Proteins play a key role in forming enzymes and hormones.
- Saturated Fatty Acids:
- Definition: Fats that contain no double bonds between carbon atoms.
- Health Impact: High intake can increase harmful LDL cholesterol, raising the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Structural Features of Xylem:
- Thick Cell Walls: Helps withstand internal pressure.
- Hollow Tubes: Facilitates the efficient transport of water.
- Pits: Allow lateral transfer of water between vessels.
- Biological Importance of Mitosis:
- Growth and Tissue Repair: Crucial for growth and replacing worn-out cells.
- Asexual Reproduction: Enables reproduction without a mate.
- Difference in Telophase Between Plant and Animal Cells:
- Animal Cells: Formation of a cleavage furrow.
- Plant Cells: Development of a cell plate into a new cell wall.
- Causes and Treatments of Cancer:
- Causes:
- Genetic Mutations: Disrupt normal cell growth and division.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to carcinogens like tobacco smoke and radiation.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, obesity, and lack of physical activity.
- Treatments:
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy particles to destroy cancer cells.
- Causes: