This comprehensive guide, titled “Geography Grade 10 Questions and Answers PDF Term 3,” aims to address the critical environmental and societal issues covered in...
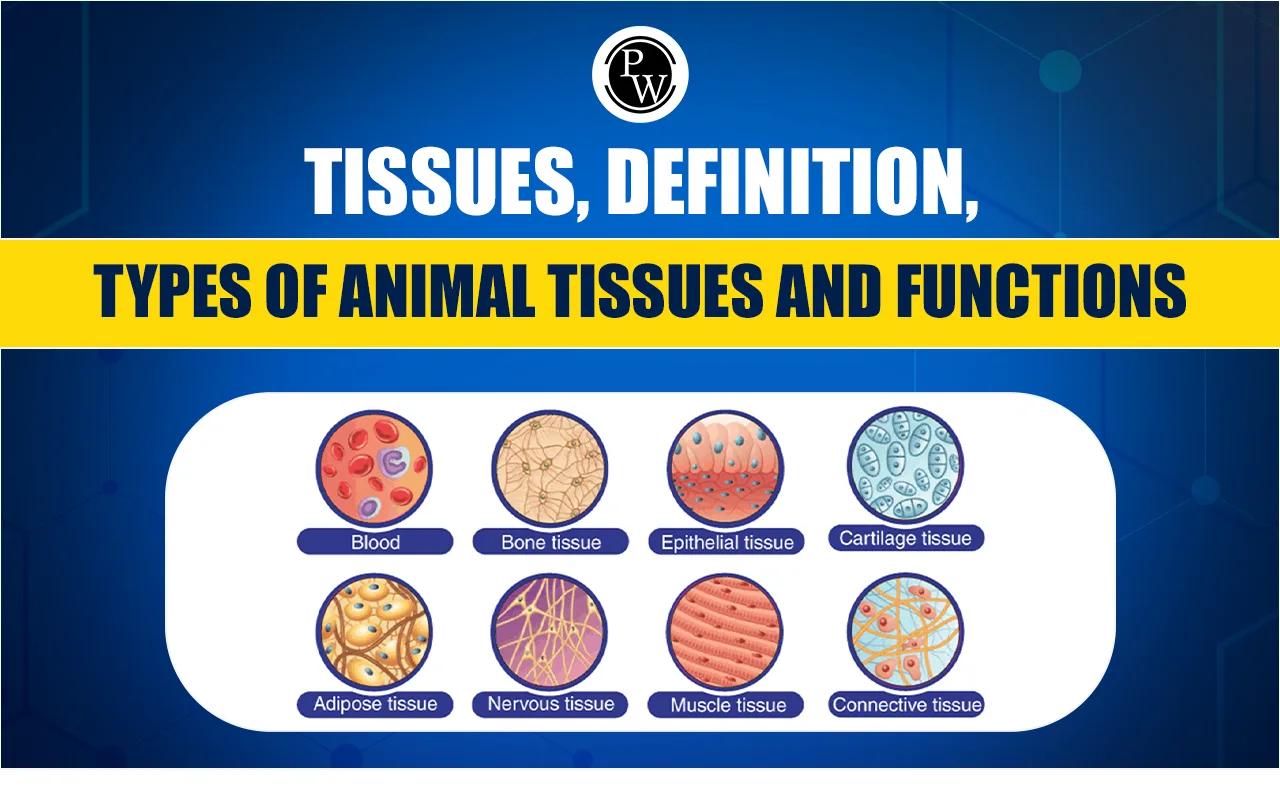
Welcome to your Grade 10 Life Sciences notes on Animal Tissues! In this section, you will learn about the different types of animal tissues, their structures, and their functions. Understanding these tissues will give you a better appreciation of how animals, including humans, are built and function.
Types of Animal Tissues
- Epithelial Tissue
- Description: Epithelial tissue covers the surfaces of the body and lines internal organs and cavities.
- Types:
- Squamous Epithelium: Flat and thin cells, found in areas like the skin and the lining of blood vessels.
- Cuboidal Epithelium: Cube-shaped cells, found in glandular tissues and kidney tubules.
- Columnar Epithelium: Tall and column-like cells, found in the digestive tract lining.
- Functions: Protection, absorption, secretion, and filtration.
- Connective Tissue
- Description: Connective tissue supports, binds, and protects other tissues and organs.
- Types:
- Loose Connective Tissue: Provides support and flexibility; found beneath the skin.
- Dense Connective Tissue: Provides strong support; found in tendons and ligaments.
- Adipose Tissue: Stores fat; found under the skin and around organs.
- Cartilage: Provides flexible support; found in the nose, ears, and joints.
- Bone: Provides rigid support and structure; forms the skeleton.
- Blood: Transports nutrients and wastes; found throughout the body.
- Functions: Binding and support, protection, insulation, and transportation of substances.
- Muscle Tissue
- Description: Muscle tissue is responsible for movement in the body.
- Types:
- Skeletal Muscle: Voluntary muscle attached to bones; responsible for body movements.
- Cardiac Muscle: Involuntary muscle found in the heart; responsible for pumping blood.
- Smooth Muscle: Involuntary muscle found in walls of internal organs; responsible for movements like peristalsis in the digestive tract.
- Functions: Movement, maintenance of posture, and heat production.
- Nervous Tissue
- Description: Nervous tissue is involved in receiving, transmitting, and processing nerve impulses.
- Components:
- Neurons: Nerve cells that transmit signals.
- Neuroglia: Supportive cells that protect and assist neurons.
- Functions: Control and communication within the body.
Importance of Animal Tissues
Understanding animal tissues is essential as it helps us learn how the body is structured and functions. Each type of tissue has a specific role, contributing to the overall health and operation of the body.
PDF Notes
- 8-Life-Sciences-Grade-10-Animal-Tissues-Worksheet-Answer (Download)
- 8-Life-Sciences-Gr-10-Worksheet-Animal-Tissues (Download)
These resources will help reinforce your understanding of animal tissues. Make sure to go through the worksheets and answer sheets to test your knowledge and prepare for your exams.
Animal Tissues: Grade 10 Life Sciences Questions and Answers Activity
1. What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
Answer: The primary functions of epithelial tissue are protection, absorption, secretion, and filtration. This tissue covers the surfaces of the body and lines internal organs and cavities.
2. True or False: Squamous epithelium is composed of cube-shaped cells.
Answer: False. Squamous epithelium is composed of flat and thin cells. Cube-shaped cells are found in cuboidal epithelium.
3. Describe the structure and location of cuboidal epithelium.
Answer: Cuboidal epithelium consists of cube-shaped cells. It is typically found in glandular tissues and kidney tubules where it plays a role in secretion and absorption.
4. Name the three types of epithelial tissue and their primary locations.
Answer:
- Squamous Epithelium: Found in areas like the skin and the lining of blood vessels.
- Cuboidal Epithelium: Found in glandular tissues and kidney tubules.
- Columnar Epithelium: Found in the digestive tract lining.
5. What are the functions of connective tissue?
Answer: The functions of connective tissue include binding and support, protection, insulation, and transportation of substances.
6. True or False: Adipose tissue stores fat and is found under the skin and around organs.
Answer: True. Adipose tissue stores fat and provides insulation and cushioning, found under the skin and around organs.
7. Explain the difference between loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue.
Answer:
- Loose Connective Tissue: Provides support and flexibility; found beneath the skin. It has a loose arrangement of fibers.
- Dense Connective Tissue: Provides strong support; found in tendons and ligaments. It has a densely packed arrangement of fibers.
8. Where is cartilage found, and what is its primary function?
Answer: Cartilage is found in the nose, ears, and joints. Its primary function is to provide flexible support and reduce friction in joints.
9. What is the role of blood as a connective tissue?
Answer: Blood transports nutrients, gases, and wastes throughout the body. It is a vital connective tissue that helps in maintaining homeostasis.
10. True or False: Skeletal muscle is an involuntary muscle found in the heart.
Answer: False. Skeletal muscle is a voluntary muscle attached to bones, responsible for body movements. Cardiac muscle is the involuntary muscle found in the heart.
11. Describe the primary function of smooth muscle tissue and where it is found.
Answer: Smooth muscle tissue is responsible for involuntary movements such as peristalsis in the digestive tract. It is found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach and intestines.
12. What distinguishes cardiac muscle from other types of muscle tissue?
Answer: Cardiac muscle is unique because it is an involuntary muscle found only in the heart. It has intercalated discs that facilitate synchronized contractions to pump blood.
13. Explain the function of neurons in nervous tissue.
Answer: Neurons are nerve cells that transmit signals throughout the body. They are essential for receiving, processing, and sending electrical impulses.
14. What is the role of neuroglia in nervous tissue?
Answer: Neuroglia are supportive cells in nervous tissue that protect and assist neurons. They provide structural support, nutrition, and aid in repair and maintenance of the nervous system.
15. Why is understanding animal tissues important for studying how the body functions?
Answer: Understanding animal tissues is important because each type of tissue has specific roles that contribute to the overall health and operation of the body. Knowledge of these tissues helps explain how the body is structured and how it functions.
16. True or False: Bone is a type of connective tissue that forms the skeleton and provides rigid support.
Answer: True. Bone is a type of connective tissue that forms the skeleton, providing rigid support and structure to the body.
17. Describe the structure and function of columnar epithelium.
Answer: Columnar epithelium consists of tall, column-like cells. It is primarily found lining the digestive tract and functions in absorption and secretion.
18. What type of connective tissue is found in tendons and ligaments, and what is its primary function?
Answer: Dense connective tissue is found in tendons and ligaments. Its primary function is to provide strong support and connection between muscles and bones.
19. How does loose connective tissue differ in structure and function from adipose tissue?
Answer:
- Loose Connective Tissue: Has a loose arrangement of fibers, provides support and flexibility, and is found beneath the skin.
- Adipose Tissue: Contains fat cells, stores fat, provides insulation and cushioning, and is found under the skin and around organs.
20. True or False: Blood is a type of muscle tissue responsible for movement.
Answer: False. Blood is a type of connective tissue responsible for transporting nutrients, gases, and wastes throughout the body.
21. Explain the importance of muscle tissue in maintaining posture and producing heat.
Answer: Muscle tissue helps maintain posture by stabilizing body positions and generating heat through muscle contractions, which is crucial for maintaining body temperature.
22. Describe the components of nervous tissue and their functions.
Answer:
- Neurons: Transmit nerve impulses, essential for communication within the body.
- Neuroglia: Support and protect neurons, provide structural support, nutrition, and maintenance.
23. How do epithelial tissues contribute to the protection of the body?
Answer: Epithelial tissues cover surfaces and line internal organs and cavities, providing a protective barrier against pathogens, physical injury, and dehydration.
24. True or False: Smooth muscle tissue is responsible for voluntary movements.
Answer: False. Smooth muscle tissue is responsible for involuntary movements such as peristalsis in the digestive tract.
25. What role does cartilage play in the joints of the body?
Answer: Cartilage provides flexible support and reduces friction in the joints, allowing for smooth movement and cushioning between bones.
26. Explain the significance of the support provided by connective tissue in the body.
Answer: Connective tissue provides structural support to the body, connecting and holding tissues and organs together, protecting internal organs, and insulating the body.
27. Name three locations where epithelial tissue can be found in the body.
Answer:
- Skin
- Lining of blood vessels
- Digestive tract lining
28. True or False: Neuroglia are nerve cells that transmit signals.
Answer: False. Neurons are the nerve cells that transmit signals. Neuroglia support and protect neurons.
29. How does understanding the different types of animal tissues help in the study of Life Sciences?
Answer: Understanding the different types of animal tissues helps in studying Life Sciences by providing insights into how the body is structured, how it functions, and how various tissues contribute to overall health and biological processes.
30. Describe the function of bone tissue in the skeletal system.
Answer: Bone tissue provides rigid support and structure to the body, forming the skeleton, protecting vital organs, and enabling movement by acting as levers for muscles.