This comprehensive guide, titled “Geography Grade 10 Questions and Answers PDF Term 3,” aims to address the critical environmental and societal issues covered in...
Welcome to your Grade 10 Life Sciences notes on Plant Tissues! This guide will help you understand the different types of plant tissues, their structures, and their functions. By the end of this section, you should have a clear understanding of how these tissues contribute to the overall functioning of plants.
Types of Plant Tissues
- Meristematic Tissues
- Description: Meristematic tissues are regions of active cell division. They are responsible for the growth of plants.
- Location: Found in the root and shoot tips (apical meristems) and in the cambium layer (lateral meristems).
- Function: These tissues help in increasing the length (primary growth) and girth (secondary growth) of the plant.
- Permanent Tissues
- Simple Permanent Tissues
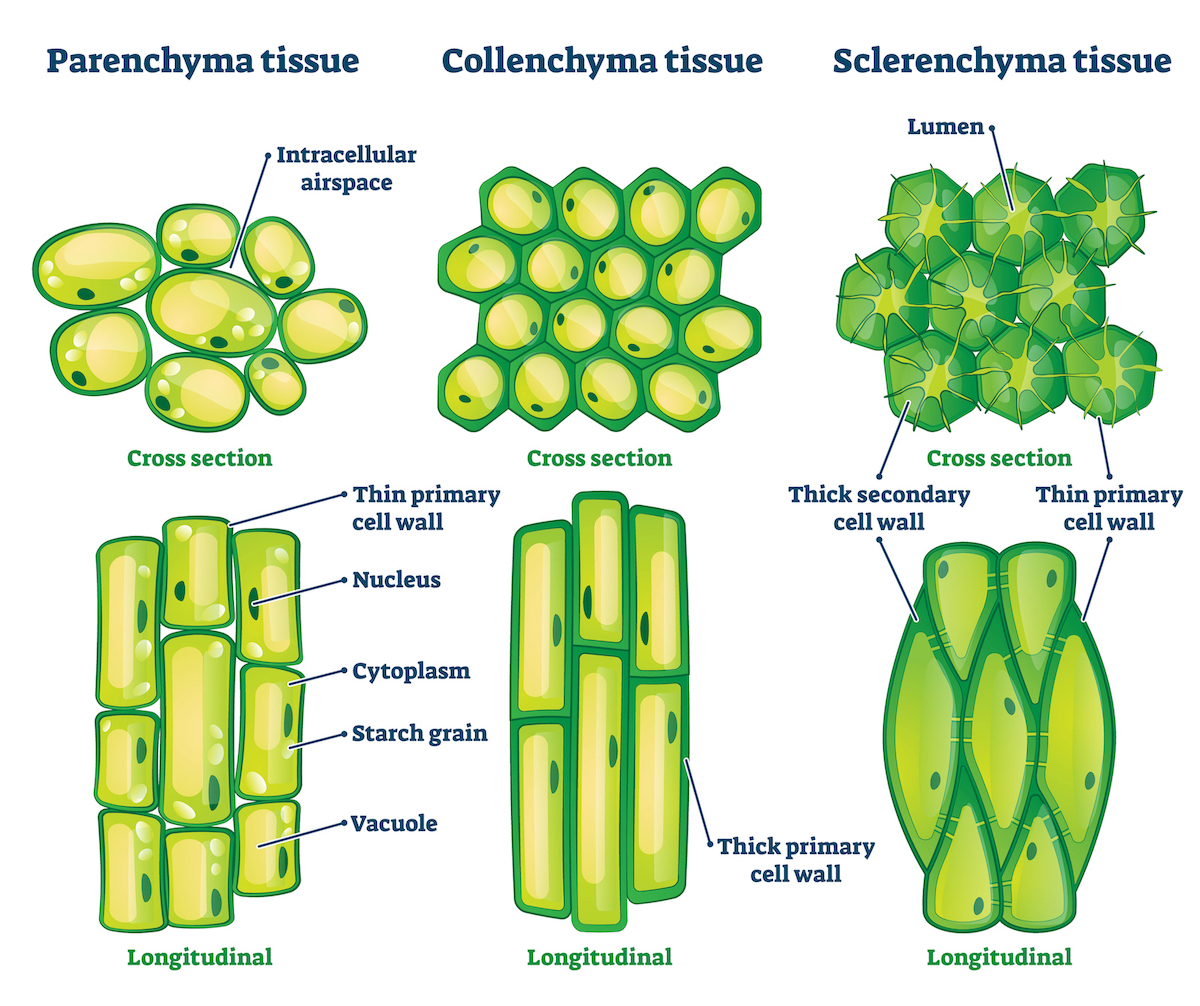
- Parenchyma:
- Structure: Made up of living cells with thin cell walls.
- Function: Involved in photosynthesis, storage, and secretion.
- Collenchyma:
- Structure: Living cells with thicker cell walls, especially at the corners.
- Function: Provides support and flexibility to the plant.
- Sclerenchyma:
- Structure: Made up of dead cells with very thick cell walls.
- Function: Provides rigidity and strength to the plant.
- Parenchyma:
- Complex Permanent Tissues
- Xylem:
- Structure: Consists of vessels, tracheids, xylem fibers, and xylem parenchyma.
- Function: Conducts water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
- Phloem:
- Structure: Composed of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma.
- Function: Transports nutrients, particularly sugars, from leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Xylem:
- Simple Permanent Tissues
Importance of Plant Tissues
Understanding plant tissues is crucial as it helps us appreciate how plants grow, develop, and respond to their environment. Each tissue type plays a specific role, ensuring the plant’s survival and reproduction.
Learn about Animal Tissues Here
PDF Downloadable Notes Resources
- 00-Life-Sciences-Grade-10-PPT-Connective-Tissues (Download)
- 00-Life-Sciences-Grade-10-Worksheet-Answer-Connective-Tissues (Download)
- 00-Life-Sciences-Grade-10-Worksheet-Connective-Tissue (Download)
- 00-LIFE-SCIENCES-GRADE-10-PLANT-TISSUES-AND-ANATOMY-OF-DICOTYLEDONOUS-PLANTS-NO-AUDIO (Download)
- Life-Sciences-Grade-10-Worksheet-1-Plant-tissues (Download)
- LIFE-SCIENCES-GRADE-10-PLANT-TISSUE-NOTES-HOMETEACHING (Download)
These resources will provide further insights and help reinforce your understanding of plant tissues. Make sure to go through the presentations and worksheets to get a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Plant Tissues: Grade 10 Life Sciences Questions and Answers
Welcome to your Grade 10 Life Sciences notes on Plant Tissues! This guide will help you understand the different types of plant tissues, their structures, and their functions. By the end of this section, you should have a clear understanding of how these tissues contribute to the overall functioning of plants.
1. What are meristematic tissues and where are they located in plants?
Answer: Meristematic tissues are regions of active cell division responsible for the growth of plants. They are found in the root and shoot tips (apical meristems) and in the cambium layer (lateral meristems).
2. True or False: Meristematic tissues are responsible for increasing the length and girth of plants.
Answer: True. Meristematic tissues help in increasing the length (primary growth) and girth (secondary growth) of the plant.
3. Describe the structure and function of parenchyma tissue.
Answer: Parenchyma tissue is made up of living cells with thin cell walls. Its functions include photosynthesis, storage, and secretion.
4. How does collenchyma tissue differ from parenchyma tissue in terms of structure and function?
Answer:
- Collenchyma tissue consists of living cells with thicker cell walls, especially at the corners, and provides support and flexibility to the plant.
- Parenchyma tissue has thin cell walls and is involved in photosynthesis, storage, and secretion.
5. True or False: Sclerenchyma tissue is made up of living cells with thick cell walls.
Answer: False. Sclerenchyma tissue is made up of dead cells with very thick cell walls and provides rigidity and strength to the plant.
6. Name and describe the two types of complex permanent tissues in plants.
Answer:
- Xylem:
- Structure: Consists of vessels, tracheids, xylem fibers, and xylem parenchyma.
- Function: Conducts water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
- Phloem:
- Structure: Composed of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma.
- Function: Transports nutrients, particularly sugars, from leaves to other parts of the plant.
7. What is the primary function of xylem tissue in plants?
Answer: The primary function of xylem tissue is to conduct water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant.
8. Explain the role of phloem tissue in plants.
Answer: Phloem tissue transports nutrients, particularly sugars, from the leaves to other parts of the plant, ensuring that all parts receive the necessary energy for growth and development.
9. True or False: Collenchyma provides rigidity and strength to the plant.
Answer: False. Collenchyma provides support and flexibility to the plant, whereas sclerenchyma provides rigidity and strength.
10. Describe the importance of understanding plant tissues in the study of Life Sciences.
Answer: Understanding plant tissues is crucial as it helps us appreciate how plants grow, develop, and respond to their environment. Each tissue type plays a specific role, ensuring the plant’s survival and reproduction.
11. Where can meristematic tissues be found in a plant?
Answer: Meristematic tissues can be found in the root and shoot tips (apical meristems) and in the cambium layer (lateral meristems).
12. True or False: Xylem tissue is involved in transporting sugars from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Answer: False. Xylem tissue is involved in conducting water and minerals. Phloem tissue is responsible for transporting sugars.
13. Explain the function of parenchyma tissue in plants.
Answer: Parenchyma tissue is involved in photosynthesis, storage of nutrients, and secretion. It plays a vital role in the overall metabolic functions of the plant.
14. How does sclerenchyma tissue support the plant?
Answer: Sclerenchyma tissue supports the plant by providing rigidity and strength through its thick, lignified cell walls, which help maintain the structure and integrity of the plant.
15. Describe the structure and function of xylem vessels.
Answer: Xylem vessels are long tubes made up of dead cells aligned end to end. They have thick cell walls and are responsible for conducting water and minerals from the roots throughout the plant.
16. What are the main components of phloem tissue, and what are their functions?
Answer:
- Sieve tubes: Transport sugars and other nutrients.
- Companion cells: Assist sieve tubes in nutrient transport.
- Phloem fibers: Provide structural support.
- Phloem parenchyma: Store and transport nutrients.
17. True or False: The cambium layer is a type of permanent tissue.
Answer: False. The cambium layer is a type of meristematic tissue responsible for secondary growth in plants.
18. Explain how collenchyma tissue contributes to the flexibility of plants.
Answer: Collenchyma tissue has cells with thickened cell walls at the corners, providing support while allowing flexibility. This flexibility enables plants to bend and withstand mechanical stress without breaking.
19. Describe the process of primary growth in plants.
Answer: Primary growth in plants involves the increase in length through the activity of apical meristems located at the root and shoot tips. This growth allows the plant to extend its roots deeper into the soil and its shoots higher into the air.
20. What is the role of lateral meristems in plant growth?
Answer: Lateral meristems, such as the cambium layer, are responsible for secondary growth, which increases the girth (thickness) of the plant. This growth strengthens the plant and supports the vascular system.
21. True or False: Parenchyma cells are dead cells with thick cell walls.
Answer: False. Parenchyma cells are living cells with thin cell walls.
22. How does understanding the function of xylem and phloem help in agricultural practices?
Answer: Understanding the functions of xylem and phloem helps in agricultural practices by ensuring proper irrigation and nutrient management, leading to healthier crops and improved yields. Knowledge of these tissues aids in diagnosing and addressing plant health issues.
23. Describe the function of meristematic tissues in plant healing.
Answer: Meristematic tissues play a crucial role in plant healing by actively dividing and generating new cells to replace damaged tissues. This regenerative ability helps plants recover from injuries and maintain growth.
24. True or False: Sclerenchyma tissue is primarily involved in photosynthesis.
Answer: False. Sclerenchyma tissue provides rigidity and strength to the plant, not photosynthesis.
25. What are the differences between apical and lateral meristems?
Answer:
- Apical Meristems: Located at the root and shoot tips, responsible for primary growth (increasing length).
- Lateral Meristems: Found in the cambium layer, responsible for secondary growth (increasing girth).
26. How does collenchyma tissue adapt to environmental stress?
Answer: Collenchyma tissue adapts to environmental stress by providing flexible support, allowing plants to bend and withstand mechanical pressure without breaking. The thickened cell walls at the corners help absorb and dissipate stress.
27. Explain the significance of simple permanent tissues in plants.
Answer: Simple permanent tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma provide essential functions such as photosynthesis, storage, support, and flexibility. These tissues contribute to the plant’s structural integrity and metabolic activities.
28. True or False: Phloem fibers are involved in the transport of nutrients in plants.
Answer: False. Phloem fibers provide structural support to the phloem tissue, while sieve tubes and companion cells are involved in nutrient transport.
29. How do complex permanent tissues differ from simple permanent tissues?
Answer: Complex permanent tissues like xylem and phloem consist of multiple cell types working together for specialized functions (water, mineral, and nutrient transport). Simple permanent tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma are composed of one type of cell and perform basic functions like support, storage, and photosynthesis.